LEVERAGING MIXED REALITY IN MITRACLIP IMPLANTATION: A PRELIMINARY CASE SERIES
Introduction
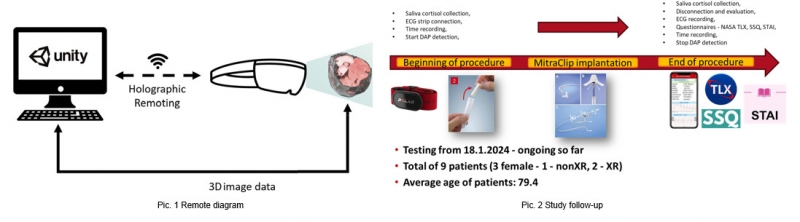
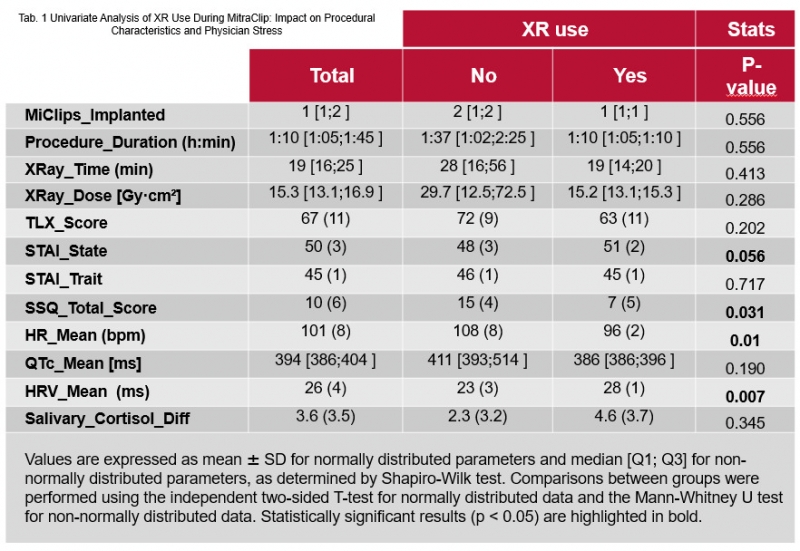
Mixed Reality (MR) technology is revolutionizing interventional cardiology by enhancing visualization and accuracy in procedures like MitraClip implantation. Utilizing Hololens 2.0 for three-dimensional DICOM data rendering improves surgeons' spatial awareness, leading to safer, more efficient procedures (see Picture 1).
Objectives
This study evaluates MR's impact on MitraClip implantation, focusing on:
Procedural efficiency
Reduced surgeon stress
Improved spatial awareness for accurate implantation
Additionally, it sets the stage for a larger pilot study.
Methods
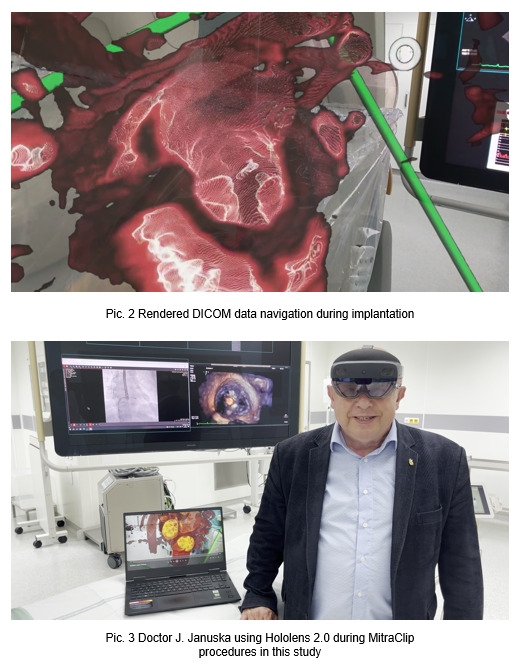
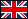
A comparative analysis of 9 MitraClip procedures was conducted, dividing them into two groups based on MR support use. Both objective (e.g., radiation exposure, cortisol levels, Picture 2) and subjective (NASA TLX, SSQ, STAI questionnaires) parameters were assessed to measure MR’s impact on outcomes and surgeon stress.
Results
Statistically significant improvements were observed:
Heart Rate (HR) Mean: Lower HR with MR (p < 0.01).
Heart Rate Variability (HRV): Higher HRV with MR, indicating reduced stress (p < 0.007).
SSQ Total Score: Lower stress/workload with MR (p < 0.031).
Although STAI State showed no significant change, trends suggest MR positively influences procedural efficiency and surgeon well-being.
Conclusion
This case series indicates MR can streamline MitraClip implantation and reduce surgeon stress. The findings justify a larger-scale pilot study (ClinicalTrials.gov ID: NCT06539416) to confirm these benefits and further investigate MR’s role in improving patient outcomes.